What Cerebellum Does
PKGhatak, MD
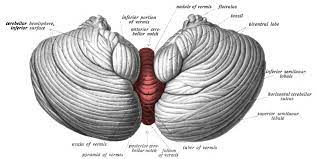
The human cerebellum occupies a small space at the back of the head, just above the neck, and it is a part of the hindbrain. Sensory information from joints, tendons and soft tissues from the limbs and trunk travel to the cerebellum. The motor stimuli coming from the cerebrum motor cortex, make connections with the nuclei of the cerebellum before reaching the lower motor nuclei of the spinal nerves and the cranial nerves. This interconnection of the motor cortex with the cerebellum results in a smooth sustained movement of the body, able to maintain the head position in space and in relation to the rest of the body and keep balance without falling. And that much knowledge people had till 1990.
Now the cerebellum is a subject of intense research for a variety of reasons.
Research in developmental biology documented three separate stages of growth of the cerebellum in humans. As the forebrain is added, the cerebral cortex, which has increased the mental faculties, knowledge gained about self, mind, higher state of consciousness, language, and development of culture has made humans as humans. But the cerebellum did not lag behind.
The growth of the cerebellum is more spectacular than the cerebral cortex. Cerebellum weighs 150 grams and contains 70 billion neurons, whereas the cerebral cortex weighs 1300 grams but contains only 16 billion neurons. The surface area of the cerebellar cortex is 1500 square centimeters, which is about 80 % of the surface area of the cerebral cortex. The cerebellar cortical folds are arranged like pages of a book - lots of surface area in a small space.
Compared with the cerebral cortex the layout of neurons and their connections in the cerebellum is much simpler and more uniform. Cerebellum receives input and sends out output to the same side of the body that is also a contrast with the cerebrum which controls the opposite side of the body. The central part of the cerebellum is old, but the lateral parts, the cerebellar hemispheres, kept pace with the growth of the cerebrum.
Cerebellum is the site of the formation and storage of working memory and the integration of automated sequences of thoughts and actions. This results in developing behavioral patterns, speech, dexterity of complex movements, a skill needed for technological advances and language development.
In association with the cerebrum, it forms kinetic memory, plans coordinated muscle movement patterns, retains reflex memory for self preservation and executes normal speech.
Cerebellum with two way communication with the thalamus and basal ganglia and receives direct input from the spinocerebellar tract and maintains balance and a stable head position both in states of body movements and at rest.
Vestibular sensory information is closely monitored by the cerebellum, that information is used to control conjugate movements of eyes, prevent double vision and reflex eye movements.
Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep includes Implicit memory involving perception and body movements. Implicit memory uses cerebellar retained memories.
*********************************


No comments:
Post a Comment