Advances in the Treatment of Parkinson's Disease
PKGhatak, MD
Parkinson's Disease (PD) is a progressive degenerating disease of the central nervous system (CNS). The cause of PD is unknown. When other conditions of the body lead to the development of symptoms similar to PD, then the condition is called Parkinson syndrome or Parkinsonism. The main causes of Parkinson's syndrome are cerebrovascular disease, small and major strokes, toxic chemicals and medications generally used to treat schizophrenia, and repeated trauma to the brain as happens in boxing and football games.
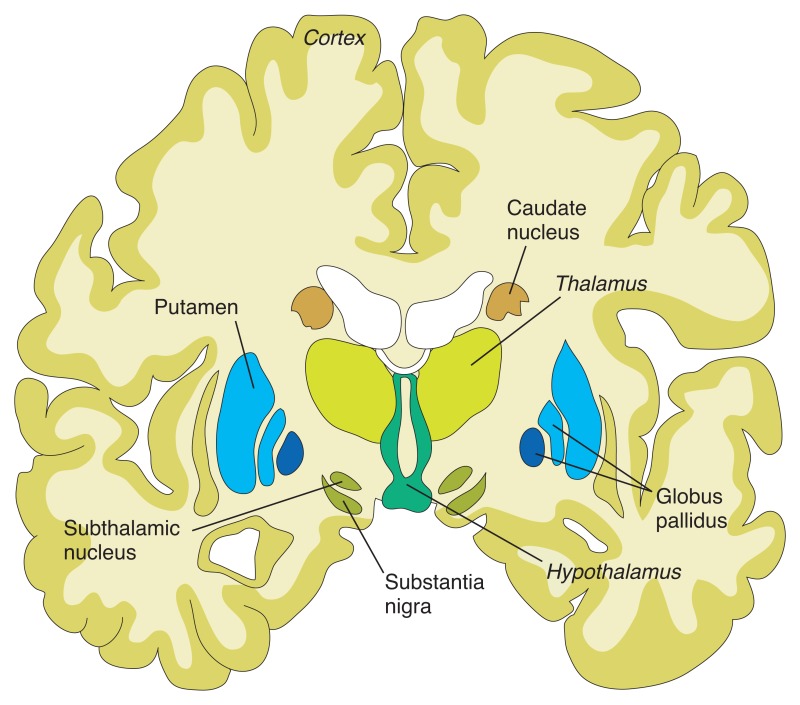
The cells in the Substantial Nigra secrete a neurotransmitter, called Dopamine, which is responsible for the coordinated and smooth functioning of voluntary movements of the body and maintaining the tone of muscles. The enzyme AAAD (aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase) converts levodopa(L-DOPA) to dopamine. The final inactive degraded product of dopamine is 3-0 methyldopamine by the action of the Catechol- 0- methyltransferase (COMT) enzyme.
Nerve cells of the peripheral nervous system and adrenal medulla and endothelial cells of the GI tract also take up L-dopa. From amino acid Tyrosine and L-dopa, the adrenal glands make dopamine, norepinephrine and adrenaline. An enzyme Monoamine oxidase (MAO) degrades dopamine, norepinephrine and adrenaline to inactive compounds. The central nervous system has no MAO and MAO cannot cross into the brain from the blood (blood brain barrier).
In Parkinson's disease substantia nigra cells die prematurely, as a result, the movements become jerky, slow and disturbance of gait and balance, tremors and stiffness develop.
Parkinson's disease clinically may appear as 3 entities initially. In Type 1- the tremors of one or more limbs predominate. Muscle rigidity is absent and ambulation remains normal. In Type 2 disease the ataxic gait and mask like face and pill rolling movements are dominant symptoms. In Type 3 cases all the typical symptoms of PD are exhibited.
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy and Lowy Body Dementia are closely related to Parkinson's disease but are not a part of this discussion.
The standard medical treatment for Parkinson's disease is to supply Dopamine and reduce or stop MAO-B activities in the body so at the end more L-dopa will be available for the brain. A group of drugs is available for that purpose and are collectively called MAO inhibitors and are in regular use in PD.
In addition, direct interventions for tremors, depression, stiffness of the body and constipation, etc. are treated with well-known medications. Physical exercise, physiotherapy, occupation therapy, speech and languages therapy are also included in the management of Parkinson's disease.
New drugs and new methods of drug delivery to CNS, Stem cell transplantation, keeping dopamine secreting cells alive and surgical treatment are parts of this article.
In between doses of medication, rescue therapy.
Levodopa is a standard drug for Parkinson's disease. It is converted into Dopamine in the brain. Levodopa therapy replenishes decreased levels of dopamine in the brain. A drug called Carbidopa is an MAO inhibitor. Carbidopa and L-dopa are combined into one pill for use in PD. But in between doses, sudden deterioration of symptoms happens due to an unexpected fall of available L-dopa in the brain cells. To prevent this from happening, several drugs are now available.
Istradefylline is marketed as Nouriazen. It is an antagonist to Adenosine A2A receptors. When this receptor is blocked the nerve cells release more gamma aminobutyric acid (GABA) which is another neurotransmitter. GABA helps to ease symptoms related to the "OFF episodes" from the sudden drop of dopamine. Istradefylline belongs to a small molecule drug and is given orally once a day dose.
Entacapone is an inhibitor of the MAO-B enzyme. Available as Comptan. Other available MAO-B inhibitors are Rasagiline and Safinamide.
New delivery system for Levodopa.
New formulation allows Levodopa delivery via inhalation. It acts quickly. It is marketed as Inbrija.
Apomorphine is a form of a thin sublingual tablet that acts quickly to counter the symptoms of off symptoms.
Accordion pills. Layers of Levodopa are designed in such a way that they will release at a slow and steady level. Thus, decrease unusual dips of drug blood levels and decreases the incidence of “off” episodes."
6. Pump
and patch pumps are also used and have improved for steady drug delivery
GDNF.
Glial cells produce a neurotrophic factor. It is a naturally occurring protein that protects many types of brain cells.
In Parkinson's disease, the GDNF is delivered directly into the substantia nigra by implanted tubes in the brain, through a port is surgically placed behind the ear. When GDNF is delivered every 4 weeks for 9 months, patients receiving this therapy show remarkable improvement and PET scans detect regeneration of dying dopamine producing cells.
Stem cell Transplantation.
In a study done at Massachusetts general hospital and Cornell Medical center, the dopamine producing stem cells were transplanted.
Pluripotent stem cells are harvested from the skin of a patient and the pluripotent cells are engineered to differentiate into dopamine generating stem cells. Then the stem cells are transfused. In this study, patients are followed for 2 years. During this follow-up period, the patients show symptomatic improvement and the transplant cells remained alive and functional.
Surgical treatment.
Deep brain stimulation by an implanted electrode in the ventrolateral nucleus of the Thalamus improves tremors in PD.
Pallidotomy. Surgical removal of palladium improves dyskinesia. In bilateral lesions, the Subthalamic nucleus is removed instead of both pallidum to avoid the development of Hemiballismus.
Radiofrequency ablation has greatly replaced surgery of the basal ganglia and achieved the same results.
Deep brain stimulation in selected groups of nuclei of the basal ganglia for various uncontrollable symptoms has become an acceptable alternative to drug therapy.
Experimental therapy.
1. Dyskinesia results from the prolonged use of levodopa. An Insulin sensitizer – MSDC0160 therapy improves dyskinesia.
2 . Anti Alpha synuclein.
Alpha synuclein naturally occurring protein, which accumulates in the cells of substantia nigra of Parkinson's patients. Several drugs are now in development stages that show promise in removing the alpha synuclein.
Recently laboratory evidence shows similar alpha synuclein protein accumulation in the nerve cells in the GI tract and a new idea is developing that the gut bacterial products or certain bacteria initiate abnormal alpha synuclein production in the gut and that process is carried to the brain either via Vagus nerve or by circulation.
A small molecule, Anle 1386 is an example of such a drug. The initial results are encouraging and show a reduction of alpha synuclein accumulation in the brain cells.
Antibody against alpha synuclein. When PD patients are treated with alpha synuclein antibodies reduction of this protein in the brain cells and the clumping of protein molecules disappear.
Vaccine to stimulate antibodies to alpha synuclein is underway.
3. Repurposed drugs. Exenatide is a diabetic drug found to protect dying brain cells in Parkinson's disease patients. Inosine – is a nucleoside, when used in humans, it increases urate levels. Urates are antioxidantsand and protect brain cells. Israpidine is a B.P drug, found to preserve brain cells. Nilotinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor and is used in Chronic myeloid leukemia, when used in Parkinson's patients, it helps clear the alpha synuclein by phagocytosis.
Treatment of the Gene mutation.
Mutation of the GBA gene causes cellular dysfunction from the accumulated of lipids in the cells. An experimental drug GZ/SAR 40267 reduces lipid accumulation in the cells.
An oral drug LTI-291 corrects Liposomal dysfunction which is the cause of lipid accumulation.
Hemanti's Neurotrophic factor. This neurotrophic factor protects cells from premature death.
Glutamate blockers.
In long term use of L-dopa in PD patients Glutamate is over expressed in neurons of basal ganglia due to phosphorylation of N-methyl D aspartate receptors and that is responsible for dyskinesia.
Foliglurax and Dipraglurant reduce Dyskinesia by blocking Glutamate in the brain.
Serotonin receptor blockers
In PD patients, in addition to the loss of dopamine producing cells in basal ganglia, serotonin producing neurons are also lost to a certain extent. As a result, serotonin terminals in basal ganglia become over abundant compared to dopamine terminals. Serotonin terminals convert L-dopa into dopamine in excess amounts and produce dyskinesia.
Serotonin
receptor blockers mitigate this problem. Example: Eltoprazines.
Anti-Choline drugs.
Acetylcholine hyperactivity in dopamine depleted brain is implicated in gait disturbance and frequent falls. Varecline and Donepezil reduce brain acetylcholine levels and reduce these complications.
In recent years many private organizations came together and made funds available for research. The progress has been impressive. Improvement in stem cell transplants and gene therapy, perhaps, one day will make Parkinson's disease a mild form of disability in case an outright cure is not possible.
***********************************************************
