Syndrome in Clinical Medicine
P.K.Ghatak,MD
In a NIH publication in 2003, Dr. Franz Calvo et al, defined syndrome as a recognizable complex of symptoms and physical findings for which a direct cause is not necessarily understood. Once the medical science identifies a causative agent or process with a high degree of certainty, physicians may then refer the process as a disease and not a syndrome.
Some well known syndromes are now called diseases and to illustrate, an example is Cushing's disease and Cushing's syndrome. In 1912, Dr. Cushing reported a new disease he called polyglandular syndrome due to malfunction of the Anterior Pituitary gland. He published this entity in 1932 as basophil adenomas of the Pituitary body and named it Pituitary basophilism. Symptoms of the disease - gained excessive weight, mostly around the back of the neck, face and abdomen. Also developed high blood pressure, diabetes, acne and facial hair. In subsequent years, the condition was known as Cushing's syndrome. Further studies identified the cause was a tumor of the anterior pituitary producing an excess amount of ACTH hormone, which in turn put out excess corticosteroids from the Suprarenal glands. Similar changes were also detected when patients took steroids for a prolonged time, as one of the anti-rejection drugs following kidney transplants. And also seen in certain cancers of the lungs secreting an excess amount of polypeptide having similar hormone like actions of the suprarenal gland. Now Cushing's Disease term is reserved for symptom complex arising from tumor of the anterior pituitary and Cushing's syndrome is applied to all other causes which can produce some features of Cushing's disease.
If one looks up Syndrome in the Wikipedia, one will be surprised to find more than 1600 syndromes. In the index of any textbook of medicine, where every entry is listed in alphabetical order, one finds only 3 entries under syndrome, the rest of the syndromes are under the first letter of a name attached to the person who discovered the illness. Not all the listed syndromes, however, follow this rule. Some names are retained because the name refers to well understood symptoms by the public, like - Milk - Alkali syndrome and Irritable Bowel Syndrome.
Recent rapid advances in genetics, MRI imaging, sonography, immunology and biochemistry have solved many obscure causes of syndromes. In the lifetime experience of any well rounded physician, they might have not seen more than 30 syndromes. Certain specialties like Pediatrics are likely to see more syndromes.
A few syndromes will be presented, one or two from each group, to give the readers a chance to the readers the mystery about the syndrome.
Down syndrome.
Down syndrome arises from abnormalities of chromosome 21. It occurs in 75% of cases as inherited and 25% as spontaneous. Each cell of the body contains an additional one full or partial copy of chromosome 21. This generally happens as non-splitting or translocation between chromosome 21 and 14 or 21 and 21 or 21 and 22. In 2 to 3 % cases it also occurs due to Mosaicism.
Some of the common features of Down syndromes are mental retardation, flat cranium and flat nose bridge, a short neck, large tongue compared with the floor of the mouth, prominent epicanthal fold, structural heart defects, truncal obesity, poor muscle tone an delayed mile stones of development.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome.
Originally, the Polycystic Ovary syndrome was called Stein-Leventhal syndrome because this pair of investigators were the first to report it in 1935. In 1990, NIH added two additional criteria - multifactorial genetic errors and insulin resistance, and finally in 2003, ultrasonographic detection of more than 20 cysts in the ovary was added and named it Polycystic ovary syndrome. The cause of this syndrome is unknown and symptoms vary widely.
A typical case has these features: Symptoms of irregular and scant menstrual flow or delayed menarche. Development of acne and facial and body hair of masculine type, obesity, hypertension and insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus. Most cases are due to excessive androgen activities, but androgen is normal in the minority of cases. In a few cases, the polycystic ovary syndrome is detected during investigation of failure to conceive. If not treated properly, there is a high likelihood of development of endometrial carcinoma later in life.
Klinefelter syndrome. This congenital condition affects only male children due to having an extra X chromosome. The condition is also known as 47 XXX. The genetic abnormality occurs randomly either in the development of the ovum or sperm. The condition is generally detected at puberty when the child failed to develop muscle mass and develop a feminine body type - gynecomastia, no facial hair and wide hips. They have small genitalia and testicles, scant or absent sperm production and have long legs and a short torso. Many have learning difficulties and lag behind in reading and writing skills.
Not all affected have all the above features and may pass as normal and only correctly diagnosed much later when one fails to father children. They carry the risk of breast and extragonadal germ cell cancers and also osteoporosis.
Turner's syndrome. Turner's syndrome is also known as 46 XO. This congenital condition is seen only in female offspring, arises due to missing a whole or part of the sex chromosome X; but whether that missing X chromosome is paternal or maternal is not known. The gene responsible for bone growth is the SHOX gene and it is missing in Turner's syndrome, resulting in the abnormalities of bones in Turner's syndrome. At birth the child may appear normal except for a web neck and a broad chest. As the child reaches age 9 or 10, the growth slows down, develops no secondary sexual characters and menstrual cycles. Other features are cubits vulgus, aortic/ pulmonary stenosis and high BP, diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism and osteoporosis.
Fragile X syndrome: It is a X link cause of mental retardation. Males are more severely affected than females. Incidence is 1:4000 male births and 1:10,000 in females. Symptoms in female are learning difficulties, variable degrees mental retardation and early onset of menopause. In males, the physical characteristics are large ears, a prominent jaw bone, a pitched voice, Mitral valve prolapse and increased immobility of joints. This syndrome is associated with autism.
The tip of the long arm of chromosome X carries the mutated Fragile RNA gene, results from undue expansion of CCG repeats. More repeats are present more mental retardation is detected.
Marfan syndrome. Marfan syndrome is an autosomal dominant inherited disorder of the connective tissue due to mutations in the Fibrillin gene (FBNA1) on chromosome 15. This results in aberrant TGFB1 and TGFB2 activities. Clinical features of Marfan syndrome are tall stature, long arms and legs, scoliosis, pigeon chest wall deformity(Pectus excavatum), dislocated eye lenses, mitral valve prolapse, aortic root dilatation, aortic incompetence and aortic aneurysm and dissection.
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. This is another connective tissue autosomal dominant inherited disorder. Mutation of many genes, the last count 20 genes, are implicated, and based on the severity of symptoms, 11 varieties are known. Those who have severe symptoms have a mutation of COL5A1 and COL5A2 genes, other mutated genes are TNXB, ADMTS2, PLOD1, FKBP14 and many others. Mutations result in the formation of collagen tissue in a haphazard fashion and functionally of poor quality specially of the skin, skeletal muscles, arteries, bones and internal organs. Major symptoms include fragile velvety skin, which peels off easily and forms extensive scars. Aneurysm of the artery and dissection and rupture of aneurysm and other changes of the eyes, heart and bones mentioned under Marfan syndrome.
Irritable bowel syndrome. Irritable bowel syndrome fits the classical definition of the syndrome. A group of symptoms originates in the colon and small intestine but the cause remains unknown. Common symptoms are - a sense of not being able to evacuate completely after a bowel movement, constipation and low grade abdominal cramps, flatulence and diarrhea, often hard and lumpy stool and diarrhea on the same day, and several bowel movements a day. Various theories are put forward, including stress, pressure of modern life, precooked meals, food additives, change of colon bacterial colonies and low tolerance to pain. Both sexes are affected and the age of onset - from teens to elderly. It is a common illness.
Milk-Alkali syndrome. It is a self made syndrome due to taking an excessive amount of Calcium supplement to prevent osteoporosis and the condition is accelerated and made worse by taking a mega dose of vitamin D3. In the previous generation, people suffered this complication from taking excessive amounts of Tums, Maalox and Mylanta for heartburn and peptic ulcer diseases. Excess alkali present in the form of carbonate in these compounds shifts the blood pH towards the alkaline side. High blood calcium results in an excess amount of calcium excreted in the urine. Kidney stones and urinary bladder stones may develop. Renal colic, chronic pain around the loin and back are usual symptoms of kidney stones. Left untreated, patients may end in renal failure.
Abdominal Compartment syndrome. This is a serious and often fatal condition that arises from several causes but is often seen in severe burn victims. Other causes are organ transplants, prolonged abdominal surgery specially repair of abdominal aorta rupture, bullet or knife penetrating injury with severe intra-abdominal hemorrhage. Sepsis, abdominal abscess, severe peritonitis and others. Fluids and inflammatory exudates accumulate in and around organs and raise intra abdominal pressure over 20 cm of Hg. This impairs arterial supply and blocks venous and lymph drainage, producing further damage to the abdominal organs. Immediate proper fluid management and abdominal surgery is needed to relieve the high intra abdominal pressure.
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS). A healthy newborn child suddenly stops breathing and dies during sleep. In the majority of cases are due to suffocation due to putting children face down in a soft bed for sleep; which favors obstruction of the mouth and nose. About 20 % of cases remain unknown.
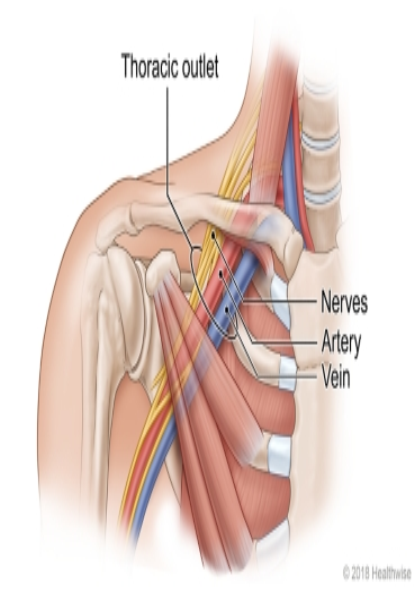
Thoracic outlet syndrome.
Just below the clavicle at a point it turns towards the shoulder, the Subclavian artery the subclavian veins and all the nerves arise from the brachial plexus, enter the chest wall and course down the medial side of the arm. There is just enough room for the structure to pass. In an abnormal situation like fracture of the clavicle and hematoma formation, a cervical rib and osteoma of the first rib that space becomes too tight for these structures and pressure on artery produce pain in the arm and hand, pressure on the vein swelling of hand and forearm and bluish discoloration of fingers, Pain over the nerve produces tingling numbness of fingers and muscle weakness. The pressure must be relieved by surgery to prevent permanent damages to the hand.
Tarsal tunnel syndrome. Just like carpal tunnel syndrome, Tarsal tunnel syndrome may develop at the ankle joint. Symptoms and causes are practically the same except for the site.
Inappropriate ADH secretion. Blood volume and serum osmolarity are maintained by feedback loops on the control center located in the hypothalamus and posterior pituitary gland. In lower blood sodium concentration and excess water content of blood (low osmolarity), no Anti Diuretic Hormone (ADH) should be released from the posterior pituitary. But if ADH is still released in such a condition, the situation is called Inappropriate ADH secretion. The causes are many, however, Lung cancer, encephalitis, meningitis, subdural hematoma are main causes.
Syndrome X. Syndrome X is due to abnormal microcirculation of the coronary arteries or coronary vasospasm, which results in Angina pectoris.
Syndrome of apparent mineralocorticoid excess, This syndrome is due to 11 beta hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency inherited on an autosomal recessive mode. Symptoms are early onset of hypertension in childhood, low serum potassium and metabolic alkalosis.
Metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome is a more recent entry in the syndrome category; previously the components of this syndrome were known as essential hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, obesity and diabetes mellitus. Under the new name, those previous entities are refined and redefined, instead of hypercholesterolemia, it is now low HDL cholesterol and high triglyceride. Obesity is now abdominal obesity, Diabetes is replaced by above impaired fasting blood glucose. People with Metabolic syndrome are at high risk of developing coronary arterial disease, diabetes mellitus and cerebrovascular accidents.
Stokes - Adam syndrome. This syndrome was well established a century ago, when physicians used their well cultivated skill of observation and taking pulse over several minutes. Main features of Stokes-Adam syndrome are sudden loss of consciousness, and fall to the ground and having epileptic seizures due to complete heart block ( third degree in new definition) and a pulse rate of 35 or below. Ventricular fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia also unconsciousness and seizures. At one time it was called Cardiac seizure and that name was better known than Stokes-Adam syndrome.
Long Q-T syndrome. This is an electrocardiogram finding. The time interval between the beginning of the q wave and the end of the T wave on the tracing of an ECG (EKG) is normally 0.43 millisecond when the heart rate is 72/ minute. In a slower heart rate, the Q-T interval increases predictably. In several cardiac diseases and quinine, procainamide, digitalis, over-the-counter cold medicines and many other medications can cause undue prolongation of Q-T interval. The longer the interval, the greater chance there is of Ventricular ectopic beats and precipitation of ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. A particular form of multifocal and multidirectional ectopic ventricular beats called Torsades des pointes (a French word, meaning twisting around points) is a forerunner of Ventricular fibrillation and death.
Torsades des pointes
Sick sinus syndrome. This is another very significant ECG finding. The natural cardiac pacemaker is the sinus node. In oxygen deprivation from any reason, electrolyte imbalance and certain medications, the sinus node fails to generate the electrical pulse wave for the heart muscle to contract. This can manifest as slow heart rate over 3 seconds, 1st, 2nd, and 3rd degree heart block. These changes are variable and in some cases variable cardiac block can be intermittent. To detect the condition, a special cardiac monitor is used, which can trace every cardiac beat and record on a preset program. This allows closer examination of any abnormal heart beat and suitable treatment can be offered – often a pacemaker. Main symptom of sick sinus syndrome is missing a heart beat, irregular pulse, palpitation, fluttering sensation in chest, confusion and loss of balance and fall.
Goodpasture syndrome. Goodpasture syndrome is an example of how an antibody, generated to fight an unidentifiable infection, mistakes its own kidneys as foreign and attacks the collagen tissue present in the basement membrane of glomeruli and walls of alveoli of lungs, results in hemorrhage in the kidney and lungs. Main symptoms are bloody urine and coughing out of blood. Other significant symptoms are shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, anemia, high BP, fatigue, nausea and vomiting. It is a major illness and requires immediate medical attention.
Alport syndrome. Alport syndrome is a multisystem inherited disorder involving collagen IV tissue and results in renal failure, deafness and visual impairment. The defective gene is carried on the X chromosome. Male child develops glomerulonephritis at an early age and progresses rapidly and unless treated, dies by age 40, females are less frequently affected and the disease progresses slowly.
Nephrotic syndrome. Nephrotic syndrome is a stage in renal failure that arises from protein losing glomerulonephritis. Presence of a large amount of protein in the urine makes urine foamy, hypoalbuminemia produces puffy eyes, pale puffy face, ankle edema and scrotal edema. With the further progression of disease, ascites and plural effusion are seen. Anemia, fatigue, weight gain from accumulated water develop. Intercurrent infection is common.
Carcinoid syndrome. In a previous blog, carcinoid syndrome was discussed in detail. See footnote.
Carcinoid syndrome is due to the production of many polypeptides which have hormone like effects released from one variety of neuroendocrine tumor. Carcinoid tumors generally arise in the small intestine, stomach, colon, appendix, rectum and liver and pancreas, and also arise in the bronchial tree of the lung. Carcinoid secretes serotonin, histamine, kallikrein, tachykinins and prostaglandin. These are potent vasodilators and produce intense vasodilatation, hypotension, watery diarrhea, asthma like bronchospasm and intense flushing of the face and body. The tumors are small and can be benign or malignant, but pathologically can not be determined whether a tumor is benign or malignant. In malignant variety, the tumor metastasizes in the liver.
Dumping syndrome. Dumping syndrome is a number of gastrointestinal symptoms that occur a few minutes after a meal. Vagotomy and reducing stomach capacity by surgery are the principal causes of Dumping syndrome. Following any such stomach surgery, the food leaves the stomach prematurely and enters the duodenum in large amounts overstretching the duodenal wall, causing upper abdominal crampy pain, sense of abdominal fullness, nausea, diarrhea, weakness and lightheadedness. And later develops palpitation and rapid heart beats.
Short bowel syndrome. Certain medical illnesses require taking out a part of the small intestine. The small intestine becomes shorter. This changes the absorptive capacity of the small intestine and patients develop loss of weight and nutritional deficiency. Crohn's disease and ischemic bowel are most common causes.
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome (Z-E Syndrome). Z-E syndrome is due to Gastrin producing tumor - Gastrinoma of the duodenum or pancreas. Gastrin stimulates gastric acid production. The majority of Z-E syndrome cases are spontaneous in origin but 25 % are due to Multiple endocrine neoplasm of type 1(MEN1). Several complications generally develop and are pretty serious – gastric perforation and profuse Gastric bleeding, esophagitis and esophageal atresia.
Budd Chiari syndrome. This syndrome is due to hepatic vein thrombosis, which produces liver enlargement, upper abdominal pain, hepatic necrosis, followed by centrilobular fibrosis and jaundice and liver failure. Patients may develop this condition due to a hypercoagulable state from inherited conditions like Factor V Leiden, Protein C and S deficiency or from acquired conditions like myeloproliferative disorders or Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria.
Sjogren syndrome. This syndrome is named after a Swedish physician, Dr Henrik Sjögren, who reported cases of chronic arthritis associated with dry eyes and dry mouth. It is an autoimmune disease producing chronic lymphocytic inflammation of salivary and lacrimal glands. The microvascular and ductal blockage results from inflammation, which produces dryness. In addition, exocrine glands of the skin, GI tract, joints, lungs, CNS and kidneys are involved. Arthritis of the hand resembles rheumatoid arthritis. ANA blood test is positive over 1:256 dilution and in addition SS-A, SS-B and RP serology are positive. Sjögren's patients run a risk of B-cell lymphoma (non-Hodgkin lymphoma) and antiphospholipid antibody production results in vascular thrombosis.
Gillian Barry syndrome. This is an example of an Autoimmune nervous system disease. Antibodies attack the myelin sheath of the peripheral nerve and the damaged sheath eventually damages the core nerve fibers of axons. Peripheral neuritis causes weakness of muscles of the limbs, muscles of respiration and face. What triggers antibody production is not known but a viral infection is likely. From the onset of symptoms of muscle weakness and tingling, numbness and pain, the disability reaches its maximum in 3 weeks, and respiratory failure develops.
Pickiwian syndrome. Nearly 200 years ago, the Author Charles Dickens in his famous publication “The posthumous papers of the Pickwick club” described obese individuals who were awake but hypoventilate due to reduced sensitivity to hypercapnia of the respiratory center and frequently dozed off. Pickiwian syndrome is chosen to honor Dickens's astute observation of human nature. People with this syndrome have a BMI over 30 kg/square M. Fat accumulates around the neck, chest, and upper abdomen, and have a blunt respiration drive even in the presence of the strongest stimulus, respiratory acidosis and hypercapnia. Leptin insensitivity explaining the reason for obesity.
Premenstrual syndrome. Million of women suffers irritability, mood changes, weight gain and puffiness of face and hands and feet before the menstrual flow begins. These symptoms are due to hormonal changes necessary to induce shedding of extra growth of the endometrium, which developed in anticipation of fertilization of an ovum and the beginning of pregnancy.
Congenital Myasthenia syndrome. This syndrome is inherited by an autosomal recessive pattern, and also rarely by an autosomal dominant mode. Weakness of muscles of the eyelids, eye muscles that move the eyes, muscles of chewing and swallowing are commonly affected. Repeated movements make weakness worse. Mutation of CHRN gene is responsible for over 50 % of cases, the rest of the cases are due to mutation of RAPSN, CHT, COLQ, DBC7 genes. Children fails to suck breast milk. Swallowing and any normal physical activities are affected. Severity of disabilities varies depending upon the mutated genes. All these genes are responsible for providing the codes of protein synthesis required for the normal functioning of the transmission of nerve signal across the neuromuscular junction.
Eaton-Lambert syndrome. Eaton-Lambert syndrome is an autoimmune disease. Immune system produces antibodies which mistakenly attack the Calcium Channels on the nerve endings. This results in fewer functional pathways for nerves to deliver signals to the effector sites involving both somatic and autonomic nervous system. In contrast with Myasthenic syndrome, repeated action improves muscle functioning. Small cell carcinoma of the lung is the most commonly responsible for this syndrome, other malignancies also can produce this syndrome. The leg muscles are commonly affected; the effects of the autonomic nervous system can be severe in the cardiovascular system and the urogenital system.
Wernicki - Korsakoff syndrome. This syndrome is a combination of Wernicke encephalopathy and Korsakoff psychosis. Chronic alcohol abuse is the underlying cause of Vitamin B1 deficiency, which is the cause of this syndrome; however, other nutritional deficiencies are associated. The symptoms are - inability to develop memory of current events, confabulation and talkativeness, lethargy, confusion and coma. MRI shows atrophy of the thalamus, hippocampus, hypothalamus and enlarged ventricles. The symptoms are reversible if treatment can be started before Wernicki encephalopathy sets in.
Ramsey Hunt syndrome. This is a special case of Shingles. The one side of the face develops palsy of lower motor neuron type and is associated with vesicular rashes on the external auditory canal, pinna, mucous membrane of the oropharynx. This is due to reactivation of Varicella - zoster virus (chicken pox virus). The symptoms are pain in the ear, deafness, tinnitus, vertigo, balance and ambulatory difficulties.
Loeffler's syndrome. Loeffler's syndrome is due to a very high eosinophil count in the blood, associated with infiltrate of eosinophils in the lung tissue producing pneumonia like symptoms and bronchospasm. In early days, it was due to ascaris lumbricoides parasitic infestation when Ascaris larvae wandered around to find their final residing place in the small intestine. The allergic reaction generated an eosinophilic immune reaction. Now other parasites are known to produce similar reactions during their tissue migration.
Waterhouse-Feldman syndrome. Waterhouse-Feldman syndrome is a real emergency situation during a meningococcal meningitis with bilateral adrenal hemorrhage due to toxemia. It produces acute adrenal insufficiency manifested as shock, hypotension, vascular collapse and cerebral, renal and pulmonary inefficiencies. Many other bacterial and viral infections are also known to produce this syndrome. Immediate intervention to normalize blood volume and tissue oxygenation must be instituted and intravenous corticosteroids are administered along with antibiotics and other therapeutic agents.
Gilbert syndrome. This is an inherited benign liver condition involving high blood unconjugated bilirubin level causing jaundice. Other parameters of liver functions are all normal and no treatment is required.
Osler-Weber- Rendo syndrome. This is also known as Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia. This is inherited in an autosomal dominant mode. It is due to the presence of multiple gene mutations. Arteriovenous malformation is present on the skin, mainly on the face and mucous membrane of the nose, mouth, stomach, GI tract, liver, lungs, spinal cord and brain. Bleeding from involved organs can produce a wide variety of symptoms, bleeding in the brain can be fatal.
Footnote: For further reading see https://humihealth.blogspot.com/Medical matters.
1. Carcinoid syndrome, - Carcinoid and Neuroendocrine tumors. Blog. Medical matters dated 13 June 2011. 2. Loeffler's syndrome. - Round worm Ascaris lumbricoides. Dec 6.2023 3. Korsakoff psychosis. - Speech disorder. Oct,16,202. 4. Sjögren syndrome. - Collagen & mixed connective Tissue diseases. Dcc14,2022. 5. Zollinger- Ellison syndrome. - Peptic ulcers. .Feb 16, 2023 .6. Polycystic Ovary syndrome. Insulin resistanceMarch10,2022. 7. Cushing's syndrome. Pituitary gland. August 20,2021. + Adrenal gland Oct22,2021. 8. Rumsey Hunt syndrome. Chicken pox Feb 16, 2023, 9. Myasthenic syndrome. Neuromusculat transmission, Dec22,2022. 10. Milk- Alkali syndrome. Kidney stones April 16, 2022.
revised; September 2025.
**********************************************************