Anatomy of the Human Soul
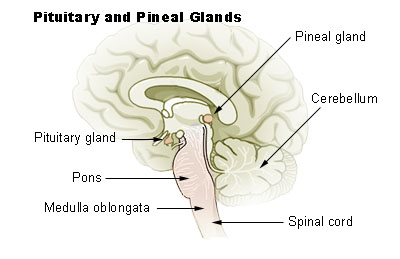
Pineal gland
PKGhatak, MD
Pineal gland.
A tiny endocrine organ in the brain that controls the circadian rhythm in humans is very much in the domain of Philosophers ever since the 17th century French nobleman Rene Descartes called the Pineal gland the site of the human soul. Today his concept of the soul residing in the pineal gland is dismissed, but the interest he generated still persists.
In the lower animal, the pineal gland acts as a light perceptive organ and is referred to as the third eye. But in the higher animals, light perception is the function of the retina. The pineal gland is also known as Conarium, Epiphysis cerebri, and Pineal body.
Descartes and the Pineal gland.
In the first book, Treatise of Man, Descartes describes a kind of conceptual model of man which consists of two ingredients, a body, and a soul. In the end, he, however, says nothing about the soul. The pineal gland plays an important role in Descartes' account. He believes body sensations, imagination and memory originate in the pineal gland and the body moves because the pineal gland directs them to do it. He sees animal spirits transformed into human bodily sensations and higher mental faculties when these animal senses reach the pineal gland via tubes, and threads, and are pressurized in ventricular cavities and directed to the pineal gland by these mechanical means.
The pineal gland, he believes, moves in three ways:
1. By the force of the soul.
2. By the spirits randomly swirling about in the ventricles
3. As a result of the stimulation of these sense organs.
In his second book, The Passion of the Soul, published in 1649, he describes things other than the body's own parts, which are perceptually present within us, belong to the soul. The soul joins all body parts and so the soul belongs to the whole body. And the pineal gland is the only organ that joins the soul with the body with threads and spirits in the nerves. Descartes does not regard the soul as the principle of life but as the principle of thought. The ultimate and the most proximate cause of passion of the soul is simply the agitation by which the spirits move the little gland in the middle of the brain. [Please see the footnote]
Anatomy.
The pineal gland is located in the middle of the midbrain on the roof of the 3rd ventricle and situated below the tail end of the corpus callosum (the body of a major bundle of nerve fibers), in between the two Thalami. The pineal gland looks like a pinecone and so it was named the Pineal gland. The pineal gland is 0.8 mm in size and weighs 0.1 gm and is about the size of a rice grain. This endocrine gland is very vascular, second only to the kidneys (per each unit of mass). The blood-brain-barrier (BBB) is absent here and the hormone is secreted directly into the blood and also in the CSF. The cerebrospinal fluid bathes this gland through a small recess of the 3rd ventricle which continues within the stalk of the pineal gland.
Chemistry of Melatonin.
The pineal gland produces and releases melatonin. Melatonin is N-acetyl 5-methoxytryptamine. The amino acid Tryptophan is the source of melatonin.
Melatonin synthesis.
Tryptophan is converted to 5-hydroxytryptophan by hydroxylation. 5-hydroxytryptophan is decarboxylated to 5-hydroxytryptamine and this product is known as Serotonin.
Serotonin is converted to melatonin in two steps -
Step 1. A rate-limiting enzyme N-acetyltransferase transfers the Acetyl group from Acetyl CoA to 5-hydroxytryptamine and converts it to N-amino-5-hydroxytryptamine.
Step 2. N-amino-5-hydroxytryptamine undergoes methylation. The methyl donor is S-adenosyl methionine and the enzyme catalyzing this reaction is O-methyltransferase. And N-methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine is produced. This molecule is melatonin.
The reactions are shown as follows-
Serotonin + Acetyl CoA → N-Acetyl serotonin. This reaction is catalyzed by an enzyme N-acetyltransferase.
N-Acetyl serotonin + S- adenosylmethionine → N-acetyl 5-ydroxyserotionin. This reaction is catalyzed by an enzyme O-methyltransferase.
Darkness induces Melatonin synthesis and release.
Darkness causes the release of Norepinephrine from the sympathetic nerve terminals of the pineal gland. The enzyme system is primed by norepinephrine and Cyclic AMP is generated. (cAMP). cAMP activates N-acetyltransferase and melatonin synthesis starts. As melatonin is forming, melatonin is secreted in the CSF and the blood. The pineal gland does not store melatonin in the gland.
If the artificial white light is of a certain strength, the effect of dark on the pineal gland ceases and no melatonin is produced or secreted. During international travel by airlines, the normal dark-light cycle is disrupted and resulting in sleep disturbances.
Breakdown of melatonin.
Melatonin is broken down in the liver by hydroxylation, then conjugated with sulfate and glucuronic acid and excreted in the urine.
Nerve supply of Pineal gland.
Somatic innervation. The 5th cranial nerve sensory nucleus, the Trigeminal ganglion, supplies nerve fibers to the stock and the gland. These fibers contain neuropeptide PACP which are vasoactive compounds. (PACP is pituitary adenylate cyclase acting polypeptide)
Autonomic innervation.
Sympathetic division nerve fibers come from the superior cervical ganglion. The parasympathetic fibers originate from the Otic and Pterygopalatine ganglia
Embryology of the Pineal gland.
In the 17th week of embryonic life, an invagination of the roof of the 3rd ventricle occurs. Initially, the pineal primordium contains Pax6 cells, arranged in a radial manner. After the neural tube fuses, the Pax6 cells rearrange into a rosette formation and then disperse in all directions. All pineal cells are derived from these progenitor Pax6 cells.
An adult pineal gland contains hormone secreting pinacocytes and microglia, astrocytes, and supporting cells. In the adult pineal gland, some progenitor cells remain. Calcium deposit in the pineal gland is common in the elderly, occasionally the entire gland may be calcified.
Role of the Photoendocrine system on the Pineal gland.
The retina of the eyes, supra-chiasmatic cells of the hypothalamus and noradrenergic sympathetic nerve fibers terminate in the pineal gland. Information about light exposure and circadian rhythmic variation is integrated into the pineal gland and regulated melatonin secretion.
Melatonin concentration in the CSF of the 3rd and 4th ventricles is higher than plasma and blood. What effect melatonin has on the neurons of the brain is not known.
Melatonin Receptors.
MT 1 and MT 2 are two types of melatonin receptors in humans. MT1 receptors are present in the suprachiasmatic cells of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, retina and hypothalamus. When Melatonin binds with MT1, it produces inhibitory effects on the pituitary, and the release of hormones is inhibited and the blood level of Prolactin falls. Through the MT1 receptors, melatonin maintains the circadian rhythmic release of hormones of other endocrine glands.
MT2 receptors are present in the retina. When retinal receptors are stimulated, Dopamine release ceases. It also allows phase shifting of the internal circadian clock to the natural earth clock of the light and dark cycle. Other effects of MT2 receptor activation are increased phagocytosis and enhanced osteoclast activities and vasodilatation.
Hallucinogenic action.
DTM (dimethyltryptamine) is a hallucinogenic compound. Only a small amount of DMT is found in the Pineal gland. This fact might have started the notion that the pineal gland is a psychic center and controller of human behavior.
Melatonin use.
Melatonin in the USA is an OTC drug (over the counter). It is available in 3 mg tablets, made solely in the laboratory. One melatonin compound. Ramelton is approved by the FDA for the treatment of insomnia, but the results are not consistent.
Indication of use.
Jet lag, Circadian rhythm disorder in the blind, Delayed sleep-wake phase sleep disorder in people who have delayed sleep and delayed wake time than required of them. In insomnia, melatonin reestablishes NON-RAM sleep. It is useful in shift workers and sleep disorders in children.
Adverse effects.
Melatonin is a safe supplement. However, it is a biological amine like Histamine and Dopamine. So, care should be taken when used with epileptic drugs, anti-platelet agents, BP medications, antidepressant drugs, immune modifying drugs, and anti-anxiety drugs.
____________________________________
Rene Descartes (1596 - 1650), a French mathematician, scientist and philosopher. He stated " Je pense, donc Je suis" (I think, therefore I am.)
Footnote: https://plato.stanford.edu/entries/pineal-gland/
********************************************************